We can’t significantly address safety concerns if we’re not looking at the most dangerous modes of transportation.

On May 9, the chairman of the House Transportation & Infrastructure Committee, Representative Sam Graves, and the chairman of the Highways and Transit Subcommittee, Representative Rick Crawford highlighted recent increases in crime reports according to FTA-tracked data. The period of time evaluated (2020-2022) represents some of the worst times for transit as agencies struggled to deliver service, ridership fell, and travel behavior changed across the country.
Transit safety is foundational to encouraging communities to utilize this public resource and enjoy its numerous benefits, including economic, environmental, and public health benefits. It is essential that federal investments protect taxpayers as they travel. Unfortunately, Representatives Graves and Crawford failed to take note of the need for safety enhancements for all modes of transportation, including modes that are far more dangerous than taking the bus.
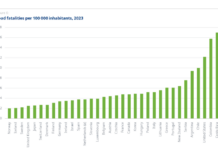
From 2020-2022, during that same period highlighted by Graves and Crawford, fatalities on our roadways exploded. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration, projected roadway fatalities increased from 39,007 to 42,795. According to Smart Growth America’s Dangerous by Design report, the number of people hit and killed while walking grew to 7,522 in 2022, marking a 40-year high.
According to the Bureau of Transportation Statistics, passenger car occupants are the primary victims in highway fatalities, totaling more than 10,000 deaths each year since 2010. By contrast, non-rail public transit occupants (like bus riders) accounted for less than 100 highway fatalities each year. Other types of public transit, like subways, accounted for less than 300 transportation-related fatalities each year. (To fully understand these numbers, it’s important to note that highway fatalities, including non-rail public transit, counted only direct fatalities like deaths that occur due to a collision. Other types of public transit included incident-related fatalities, and so these deaths are likely overstated in comparison.)
Whether we’re driving, biking, walking, or taking public transit, we should be able to travel safely. But when representatives like Crawford derail the conversation to “shine a light” on transit security alone, it unnecessarily discourages and scares individuals from riding public transportation, despite it being statistically safer than operating a private vehicle.
Increased operations funding can help support transit agencies’ efforts to improve safety. Hiring transit ambassadors and having security officers on board are just two interventions that would support crime mitigation efforts. Collaborating with local services to support housing and mental health could help address criminal activity from multiple angles.

Safety must be a priority—no matter how we travel
We’re glad federal representatives are having conversations about transportation safety, and we hope to see these conversations translate into increased funding for transit operations and security. But to truly address dangerous travel conditions, we need to consider the full picture. We hope to see additional efforts to address the top contributor to transportation-related fatalities in the US: private vehicles on high-speed roads.
Find out how we can enhance safety for all road users by improving street design. Read Dangerous by Design here.
The post We need to expand the conversation on transportation safety appeared first on Transportation For America.