Equitable enforcement of traffic rules is a major national discussion. But under-discussed is the role dangerously-designed streets play in putting Black and brown people in a perilous position: break traffic law and risk interacting with police, or put themselves in harm’s way when navigating unsafe infrastructure. Here’s our recap on a recent House hearing on equitable enforcement of traffic rules.

Last week, the House Transportation and Infrastructure Committee’s Subcommittee on Highways and Transit held a hearing on equity in traffic safety enforcement. The hearing mostly covered data on racial profiling in traffic stops and how to equip our law enforcement officers with tools to identify their implicit bias and learn how to manage it when conducting traffic stops.
While these topics are extremely important, the Transportation and Infrastructure Committee doesn’t have jurisdiction over improving the relationship law enforcement has with communities of color. However, it does have jurisdiction over solutions to unsafe street design in these communities that lead to more traffic-related stops between law enforcement and people of color.
For example, take the story of Rodney Reese: a Black high schooler in Texas who was arrested and charged for “being a pedestrian in the roadway” as he walked home from work. Rodney had no choice but to walk in the street because the sidewalk was too icy to safely walk on. He spent a night in jail.
Racism and bias likely led these officers to arrest and charge a high schooler for walking home from work. But, the question that the subcommittee has jurisdiction over is why was this high schooler walking in the roadway in the first place and what can this committee do about it?
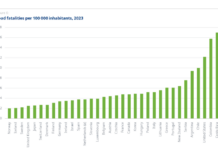
According to Smart Growth America’s report Dangerous by Design, Black Americans were 72 percent more likely to be struck and killed while walking compared to people who don’t identify as Black in the past decade. Black people are also much more likely to be stopped, ticketed, and arrested for jaywalking
Stories like Rodney’s are quite common in marginalized communities where underinvestment has led to unsafe, high-speed street design that make walking and biking all but impossible. Vulnerable communities are often put in an impossible predicament to break the law and put themselves at legal risk to get to work, school or a doctor’s appointment or choose another option that may not be as convenient, cost more money or time.
Safe street design benefits everyone, especially marginalized communities by making it easier to bike, walk, and access transit stops. This can reduce the number of traffic infractions and therefore the number of interactions communities have with law enforcement for traffic related stops. Transportation for America implores the committee to continue to have these conversations and focus on building marginalized communities back better by investing in them. Not only does investing in safe street design prevent communities from having unwanted interactions with law enforcement, it’s also better for economic development. Streets designed to accommodate (slow) drivers, people walking and biking, and transit riders creates thriving communities by attracting businesses and connecting communities to jobs.
Here are a few things the committee can do to improve equity for communities of color and begin to reverse underinvestment in safe streets infrastructure or Black and brown communities:
- Require USDOT to collect locations of all collisions resulting in death or serious injury, highlighting those involving cyclists and pedestrians, and produce a detailed map of an annual High Injury Network and update the Fatality Analysis Reporting Systems (FARS) accordingly. Better data, and detailed maps of dangerous corridors can help communities target investments to improve safety, and in those communities most impacted by unsafe designs.
- Identify changes to the process for compiling FARS data so that the release of annual data can occur in the half of each calendar year. FARS data is not available on a regular, predictable, schedule. This undermines its utility for the public and local DOTs.
- Require the Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) and the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) to issue guidance to states and metropolitan planning organizations (MPOs), instructing them not to set safety targets that would be higher than the existing level of pedestrian and cyclist fatalities, as many states have routinely done under the current performance management system.
- Require USDOT issue guidance for determining how investments impact racial and economic equity and to use this guidance as a criterion for discretionary grant programs;
- Approve the Complete Streets Act of 2021, which creates state complete streets programs and provides funding and technical assistance to develop and construct projects, with a focus on equity and connections to jobs and services;
The INVEST Act, which passed the House in the 116th Congress, made great strides in moving the needle on these issues by incorporating a focus on safety throughout all federal programs and overhauling a broken system that allows states to increase pedestrian death without penalty. It also dedicates more funding to protect vulnerable communities and sets speed limits to prioritize safety over speed.
We want to see Congress build on the INVEST Act and are calling on the House and Senate to fundamentally reform our surface transportation. Continuing on a path of status quo will only exacerbate the inequities our most vulnerable communities face every day.
The post Unsafe streets in marginalized communities leads to inequitable traffic enforcement appeared first on Transportation For America.